
农学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 16 ›› Issue (1): 48-56.doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas2024-0182
于子涵1,2( ), 韩熙1,2, 吴晓玲1,2, 肖光莉2(
), 韩熙1,2, 吴晓玲1,2, 肖光莉2( ), 王盈1,2, 陈玉红1,2
), 王盈1,2, 陈玉红1,2
收稿日期:2024-09-27
修回日期:2024-12-15
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2026-01-15
通讯作者:
作者简介:于子涵,男,1994年出生,河南洛阳人,助理工程师,硕士,研究方向:土壤生态研究。通信地址:611133 四川省成都市温江区科惠路一段919号1栋,Tel:028-61509500,E-mail:13838441626@163.com。
基金资助:
YU Zihan1,2( ), HAN Xi1,2, WU Xiaoling1,2, XIAO Guangli2(
), HAN Xi1,2, WU Xiaoling1,2, XIAO Guangli2( ), WANG Ying1,2, CHEN Yuhong1,2
), WANG Ying1,2, CHEN Yuhong1,2
Received:2024-09-27
Revised:2024-12-15
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-15
摘要:
本研究聚焦于川东南地区不同品种水稻中镉的转运积累特征,旨在为该区域轻度Cd污染稻田的稻米安全生产提供理论依据。研究选取四川省隆昌市8个当地主栽水稻品种作为试验材料,运用田间小区试验方法开展研究。先测定水稻的农艺性状和各部位Cd含量,进而分析各品种水稻Cd富集和转运特征,最终筛选出适种的Cd低累积水稻品种。研究结果表明,8个水稻品种的农艺性状存在显著差异,且均处于相应品种理论产量范围之内;除‘内香优3号’、‘内香优5号’和‘泰优2903’外,水稻不同部位的Cd富集能力排序为籽粒>叶片>秸秆>根系。在Cd富集能力方面,8个品种中仅‘泰优2903’籽粒中Cd含量低于标准限值(0.20 mg/kg),符合国家食品污染物限量标准(GB 2762—2022)。同时,该品种的富集系数BCF籽粒和转运系数TF籽粒/叶片低于其他水稻品种。在转运系数方面,除‘内香优5号’和‘内香优8号’外,转运系数表现为TF叶片/秸秆>TF籽粒/叶片>TF秸秆/根。相关性分析表明水稻籽粒与秸秆中的Cd含量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),籽粒Cd含量分别与TF秸秆/根、TF籽粒/叶片呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。基于以上研究结果,推荐在轻度Cd污染区域推广种植‘泰优2903’,同时可通过合理搭配肥料等措施提高其产量。
于子涵, 韩熙, 吴晓玲, 肖光莉, 王盈, 陈玉红. 川东南地区不同水稻品种镉转运积累特征研究[J]. 农学学报, 2026, 16(1): 48-56.
YU Zihan, HAN Xi, WU Xiaoling, XIAO Guangli, WANG Ying, CHEN Yuhong. Research on Characteristics of Cadmium Translocation and Accumulation in Different Rice Cultivars in Southeastern Sichuan Region[J]. Journal of Agriculture, 2026, 16(1): 48-56.
| 水稻品种 | 株高/cm | 产量/(kg/hm2) | 穗粒数/粒 | 结实率/% | 千粒重/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 108.3±1.2 b | 7915±206.09 ab | 188±14 b | 80.4±0.5 a | 23.9±0.2 c |
| R2 | 115.9±2.0 a | 7585±257.10 bc | 166±17 c | 71.7±0.5 d | 25.4±0.4 c |
| R3 | 118.7±0.9 a | 7710±347.38 bc | 174±23 bc | 78.0±0.4 b | 24.2±0.5 c |
| R4 | 102.7±2.0 bc | 7685±203.16 bc | 173±14 bc | 74.6±0.2 c | 30.0±0.6 a |
| R5 | 106.9±2.4 b | 6960±392.40 c | 224±26 ab | 75.0±0.9 c | 29.0±0.6 ab |
| R6 | 95.0±1.5 d | 8720±208.81 a | 241±14 a | 81.3±0.4 a | 27.5±0.6 b |
| R7 | 97.3±2.6 d | 6965±277.85 c | 224±19 ab | 73.7±1.5 cd | 21.7±0.4 d |
| R8 | 102.5±1.5 c | 8045±212.19 ab | 196±14 b | 74.7±1.0 c | 27.6±1.1 b |
| 水稻品种 | 株高/cm | 产量/(kg/hm2) | 穗粒数/粒 | 结实率/% | 千粒重/g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 108.3±1.2 b | 7915±206.09 ab | 188±14 b | 80.4±0.5 a | 23.9±0.2 c |
| R2 | 115.9±2.0 a | 7585±257.10 bc | 166±17 c | 71.7±0.5 d | 25.4±0.4 c |
| R3 | 118.7±0.9 a | 7710±347.38 bc | 174±23 bc | 78.0±0.4 b | 24.2±0.5 c |
| R4 | 102.7±2.0 bc | 7685±203.16 bc | 173±14 bc | 74.6±0.2 c | 30.0±0.6 a |
| R5 | 106.9±2.4 b | 6960±392.40 c | 224±26 ab | 75.0±0.9 c | 29.0±0.6 ab |
| R6 | 95.0±1.5 d | 8720±208.81 a | 241±14 a | 81.3±0.4 a | 27.5±0.6 b |
| R7 | 97.3±2.6 d | 6965±277.85 c | 224±19 ab | 73.7±1.5 cd | 21.7±0.4 d |
| R8 | 102.5±1.5 c | 8045±212.19 ab | 196±14 b | 74.7±1.0 c | 27.6±1.1 b |
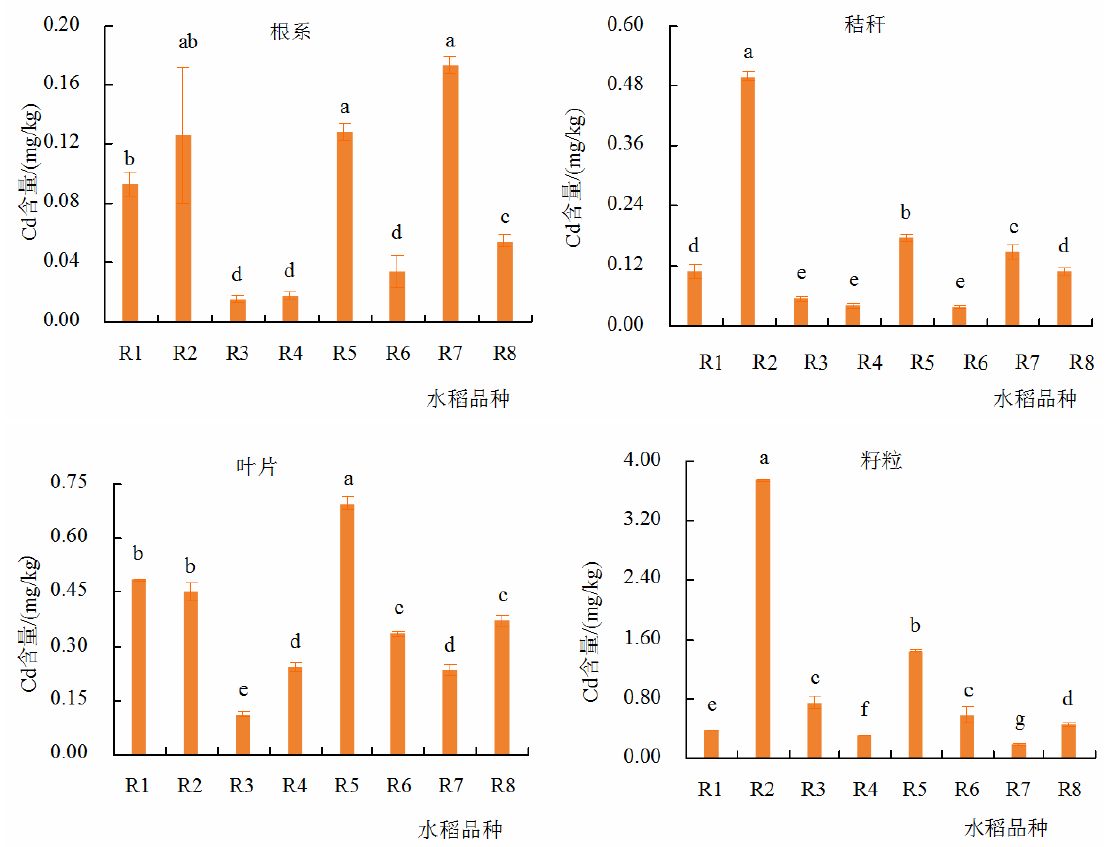
| 指标 | 根Cd | 秸秆Cd | 叶片Cd | 籽粒Cd | TF秸秆/根 | TF叶片/秸秆 | TF籽粒/叶片 | 产量 | 穗粒 | 结实率 | 千粒重 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根Cd | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 秸秆Cd | 0.573 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 叶片Cd | 0.467 | 0.393 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 籽粒Cd | 0.318 | 0.934** | 0.385 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| TF秸秆/根 | -0.108 | 0.612 | -0.228 | 0.744* | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| TF叶片/秸秆 | -0.533 | -0.610 | 0.066 | -0.457 | -0.514 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| TF籽粒/叶片 | -0.066 | 0.626 | -0.152 | 0.777* | 0.942** | -0.547 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| 产量 | -0.687 | -0.312 | -0.224 | -0.159 | 0.011 | 0.651 | -0.043 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 穗粒 | 0.283 | -0.330 | 0.257 | -0.365 | -0.749* | 0.442 | -0.567 | 0.055 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| 结实率 | -0.472 | -0.637 | -0.091 | -0.504 | -0.426 | 0.665 | -0.295 | 0.652 | 0.339 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| 千粒重 | -0.476 | -0.175 | 0.330 | 0.031 | -0.023 | 0.571 | -0.172 | 0.227 | 0.019 | -0.050 | 1 | |||||||||||
| 指标 | 根Cd | 秸秆Cd | 叶片Cd | 籽粒Cd | TF秸秆/根 | TF叶片/秸秆 | TF籽粒/叶片 | 产量 | 穗粒 | 结实率 | 千粒重 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 根Cd | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 秸秆Cd | 0.573 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 叶片Cd | 0.467 | 0.393 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 籽粒Cd | 0.318 | 0.934** | 0.385 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| TF秸秆/根 | -0.108 | 0.612 | -0.228 | 0.744* | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| TF叶片/秸秆 | -0.533 | -0.610 | 0.066 | -0.457 | -0.514 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| TF籽粒/叶片 | -0.066 | 0.626 | -0.152 | 0.777* | 0.942** | -0.547 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| 产量 | -0.687 | -0.312 | -0.224 | -0.159 | 0.011 | 0.651 | -0.043 | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| 穗粒 | 0.283 | -0.330 | 0.257 | -0.365 | -0.749* | 0.442 | -0.567 | 0.055 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| 结实率 | -0.472 | -0.637 | -0.091 | -0.504 | -0.426 | 0.665 | -0.295 | 0.652 | 0.339 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| 千粒重 | -0.476 | -0.175 | 0.330 | 0.031 | -0.023 | 0.571 | -0.172 | 0.227 | 0.019 | -0.050 | 1 | |||||||||||
| [1] |
陈卫平, 杨阳, 谢天, 等. 中国农田土壤重金属污染防治挑战与对策[J]. 土壤学报, 2018, 55(2):261-272.
|
| [2] |
张璐瑶, 赵科理, 傅伟军. 电子垃圾拆解区土壤-农作物系统中镉元素的空间分布特征及其风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(9):4432-4440.
|
| [3] |
徐双圆, 朱家辉, 王栋茹, 等. 植物套作系统修复镉污染农田土壤的效应——以苏南地区为例[J]. 中国环境科学, 2024, 44(6):3289-3300.
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154880 URL |
| [6] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166608 URL |
| [7] |
环境保护部, 国土资源部. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[R]. 北京: 环境保护部国土资源部, 2014.
|
| [8] |
doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150322 URL |
| [9] |
和君强, 贺前锋, 刘代欢, 等. 土壤镉食品卫生安全阈值景影响因素及预测模型——以长沙某地水稻土为例[J]. 土壤学报, 2017, 54(5):1181-1194.
|
| [10] |
倪中应, 章明奎, 王京文, 等. 水稻不同生育期镉吸收与积累特征研究[J]. 农学学报, 2020, 10(3):49-54.
doi: 10.11923/j.issn.2095-4050.cjas19010012 |
| [11] |
邹家素, 李晓, 万伟, 等. 重庆市某典型区域土壤和水稻中重金属含量跟踪验证研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 2020, 32(9):91-96.
|
| [12] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131366 URL |
| [13] |
项佳敏, 谢国雄, 章明奎. 镉低积累品种与调理剂降低黑色岩系农田水稻镉吸收的效果[J]. 江西农业学报, 2020, 32(7):12-16.
|
| [14] |
林小兵, 陈国钧, 周利军, 等. 南方典型稻田土壤-水稻系统环境质量评价[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2024, 24(16):6973-6979.
|
| [15] |
喻华, 秦鱼生, 陈琨, 等. 水稻土镉形态分布特征及其生物效应研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2017, 30(2):452-457.
|
| [16] |
章飞翔, 陈新友, 董力军, 等. 酸性土壤背景下不同品种水稻对镉的吸收差异分析[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2023, 50(2):319-325.
|
| [17] |
黄雁飞, 黄玉溢, 陈桂芬, 等. 桂西北岩溶区大田条件下不同水稻品种的镉累积特征[J]. 西南农业学报, 2022, 35(8):1929-1937.
|
| [18] |
鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版)[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2005.
|
| [19] |
环境保护部. HJ 803-2016,土壤和沉积物12种金属元素的测定王水提取-电感耦合等离子体质谱法[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2016.
|
| [20] |
谢燕湘, 郭志忠, 李兆敏, 等. 南方某市2012年市售大米镉污染状况及膳食暴露评估[J]. 海峡预防医学杂志, 2014, 20(1):5-6.
|
| [21] |
doi: 10.1002/jpln.v169:2 URL |
| [22] |
王刚, 孙梦飞, 钟雪梅, 等. 镉胁迫下不同水稻品种镉的累积与产量差异比较[J]. 中国农学通报, 2017, 33(17):76-81.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb17010090 |
| [23] |
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.09.057 URL |
| [24] |
doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60218-7 URL |
| [25] |
陈巧茂, 张玉盛, 黄澳琪, 等. 水稻镉污染防治及营养调控研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(16):118-123.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2023-0189 |
| [26] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109584 URL |
| [27] |
李文博, 廖启林, 范健, 等. 江苏太湖地区水稻全株Cd、Hg、Pb分布富集特征[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2025, 44(2):330-341.
|
| [28] |
郭超, 王萍, 姚茂明, 等. 贵州省山丘区谷地及河流阶地稻田耕层土壤重金属含量田块分异研究[J]. 山地农业生物学报, 2021, 40(1):22-27.
|
| [29] |
林承奇, 蔡宇豪, 胡恭任, 等. 闽西南土壤-水稻系统重金属生物可给性及健康风险[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(1):359-367.
|
| [30] |
刘侯俊, 梁吉哲, 韩晓日, 等. 东北地区不同水稻品种对Cd的累积特性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(2):220-227.
|
| [31] |
江川, 朱业宝, 陈立喆, 等. 不同基因型水稻糙米对镉、铅的吸收特性[J]. 福建农业学报, 2019, 34(5):509-515.
|
| [32] |
王成尘, 田稳, 向萍, 等. 土壤-水稻/小麦重金属吸收机制与安全调控[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(2):794-807.
|
| [33] |
龚伟群, 李恋卿, 潘根兴. 杂交水稻对Cd的吸收与籽粒积累:土壤和品种的交互影响[J]. 环境科学, 2006, 27(8):1647-1653.
|
| [34] |
杜瑞英, 文典, 赵迪, 等. Cd、Pb和As在不同品种水稻籽粒中的富集特征研究[J]. 生物技术进展, 2016, 6(2):85-90.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2341.2016.02.02 |
| [35] |
张标金, 罗林广, 魏益华, 等. 不同基因型水稻镉积累动态差异分析[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015, 31(9):25-30.
doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.2014-2566 |
| [36] |
吕本春, 杨志新, 付利波, 等. 水稻品种对镉砷累积的差异研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2023, 36(2):224-233.
|
| [37] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111198 URL |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.113970 URL |
| [39] |
冯爱煊, 贺红周, 李娜, 等. 基于多目标元素的重金属低累积水稻品种筛选及其吸收转运特征[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2020, 37(6):988-1000.
|
| [1] | 王兴福, 杨军章, 禹智, 徐章强, 罗鸣. 有机肥替代化肥对云南绥江雪茄烟叶生长和产质量的影响[J]. 农学学报, 2025, 15(8): 47-52. |
| [2] | 张虎, 吴月娥, 段海燕. 水稻氮利用效率相关功能基因研究现状[J]. 农学学报, 2025, 15(8): 6-12. |
| [3] | 王金秀, 刘家斌, 林琪, 刘义国, 周圆, 段文萍, 耿兴华, 李玲燕, 师长海. 播期对藜麦农艺性状、产量和品质的影响[J]. 农学学报, 2025, 15(7): 1-7. |
| [4] | 李建丽, 王思来, 邹书, 张海清, 相章嫩, 普伟, 张玉娇, 黄光福. 云南高光效常规水稻品种株型研究[J]. 农学学报, 2025, 15(6): 10-15. |
| [5] | 宋肖琴, 陈国安, 陈福明, 叶正钱. 不同水分管理措施对中度镉污染农田水稻吸收和积累镉的影响[J]. 农学学报, 2025, 15(6): 42-49. |
| [6] | 孙旭, 陈月珍, 陈晨, 王俐翔, 危咏菊, 孙悦华, 李亚鹏, 刘佩卓, 王广龙, 熊爱生. 淮安地区秋冬茬芹菜农艺性状、光合参数及品质性状比较分析[J]. 农学学报, 2025, 15(6): 65-70. |
| [7] | 胡勇, 陈仕红, 聂忠扬, 叶照春, 刘红峰, 宋泆洋, 王博. 烟田行间不同生草模式的控草效果及其对烟草农艺性状的影响[J]. 农学学报, 2025, 15(5): 20-23. |
| [8] | 侯意龙, 马睿岐, 李征, 石武良, 李斌, 张生武, 曹宁, 崔金虎, 张玉斌. 基于文献计量分析的土壤质量评价最小数据集(MDS)研究热点分析及展望[J]. 农学学报, 2025, 15(5): 48-61. |
| [9] | 杨进成, 胡新州, 陶春红, 李艳兰, 普加富, 安建南, 柏跃才, 毛冬梅, 刘坚坚, 杨红运, 李祥, 郭世明, 安正云, 史兰芬. 不同播期、密度、施N量对山地菜苔油菜农艺性状和产量效益的影响[J]. 农学学报, 2025, 15(2): 1-7. |
| [10] | 杨荣教, 王白, 王白昌, 张碧胜, 李学梅, 夏再兴, 余选礼, 陈以相. 两个优质软米新品种田间抗病丰产试验[J]. 农学学报, 2025, 15(12): 8-14. |
| [11] | 李明艳, 史雷, 徐伟洲, 韩侠, 乔雨, 卜耀军. 不同氮磷配施对榆阳区青贮玉米农艺性状与品质的影响[J]. 农学学报, 2025, 15(10): 1-9. |
| [12] | 吕佳佳, 初征, 郭立峰, 李宇光, 刘旭, 丁海玖, 王秋京, 周宝才. 寒地水稻开花期多雨寡照复合逆境灾损评估指标[J]. 农学学报, 2024, 14(9): 46-53. |
| [13] | 于艳敏, 武洪涛, 刘海英, 徐振华, 吴立成, 杨忠良, 张书利, 高大伟, 闫平. 水稻品种恶苗病抗性评价与筛选[J]. 农学学报, 2024, 14(7): 1-5. |
| [14] | 董洁, 火顺利, 赵双印, 张蓓, 蔡恩格力, 赵禹. 天然富硒土壤上加工番茄硒富集能力及品质分析[J]. 农学学报, 2024, 14(7): 67-72. |
| [15] | 陈淑慰, 郑伟才, 李昀哲, 罗敏, 王鸿昌, 莫坚强, 郑芝波. 紫色叶片水稻在“稻田画”应用中的品种筛选研究[J]. 农学学报, 2024, 14(6): 93-100. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||